|
Expansion of Hong Kong International Airport into a Three-Runway System |


Contents
The “Expansion of Hong Kong International Airport into a Three-Runway System” (the Project) serves to meet the future air traffic demands at Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA). On 7 November 2014, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report (Register No.: AEIAR-185/2014) for the Project was approved and an Environmental Permit (EP) (Permit No.: EP-489/2014) was issued for the construction and operation of the Project.
Airport Authority Hong Kong (AAHK) commissioned Mott MacDonald Hong Kong Limited (MMHK) to undertake the role of Environmental Team (ET) for carrying out the Environmental Monitoring & Audit (EM&A) works during the construction phase of the Project in accordance with the Updated EM&A Manual (the Manual).
This is the 17th Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report for the Project which summarizes the monitoring results and audit findings of the EM&A programme during the reporting period from 1 to 31 May 2017.
Key Activities in the Reporting Period
The key activities of the Project carried out in the reporting period included five deep cement mixing (DCM) contracts, two advanced works contracts, and a reclamation contract. The DCM contracts involved DCM works and trials, site office establishment, and laying of geotextile and sand blanket. The advanced works contracts involved cable diversion associated works, and horizontal directional drilling (HDD) works. The reclamation contract involved site office establishment and laying of sand blanket.
EM&A Activities Conducted in the Reporting Period
The monthly EM&A programme was undertaken in accordance with the Manual of the Project. During the reporting period, the ET conducted 36 sets of construction dust measurements, 23 sets of construction noise measurements, 12 events of water quality measurements, two complete sets of small vessel line-transect surveys and five days of land-based theodolite tracking survey effort for Chinese White Dolphin (CWD) monitoring and waste monitoring. Construction works on Sheung Sha Chau Island was suspended during the ardeid’s breeding season (between April and July). The ecological monitoring is therefore suspended.
Weekly site inspections of the construction works were carried out by the ET to audit the implementation of proper environmental pollution control and mitigation measures for the Project. Bi-weekly site inspections were also conducted by the Independent Environmental Checker (IEC). Observations have been recorded in the site inspection checklists and provided to the contractors together with the appropriate follow-up actions where necessary.
On the implementation of Marine Mammal Watching Plan (MMWP), silt curtains were in place by the contractors for laying of sand blanket and dolphin observers were deployed in accordance with the plan. On the implementation of Dolphin Exclusion Zone (DEZ) Plan, dolphin observers at 10 to 12 dolphin observation stations were deployed for continuous monitoring of the DEZ by all contractors for DCM and water jetting works for submarine cable diversion in accordance with the DEZ Plan. Trainings for the proposed dolphin observers were provided by the ET prior to the aforementioned works, with the training records kept by the ET. From the contractors’ MMWP observation records and DEZ monitoring records, no dolphin or other marine mammals were observed within or around the silt curtains or the DEZs in this reporting month. Audits of acoustic decoupling for construction vessels were also carried out by the ET.
On the implementation of the Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for High Speed Ferries of SkyPier (the SkyPier Plan), the daily movements of all SkyPier high speed ferries (HSFs) in May 2017 were in the range of 91 to 97 daily movements, which are within the maximum daily cap of 125 daily movements. A total of 864 HSF movements under the SkyPier Plan were recorded in the reporting period. All HSFs had travelled through the Speed Control Zone (SCZ) with average speeds under 15 knots (7.8 to 14.0 knots), which were in compliance with the SkyPier Plan. Four ferry movements with minor deviation from the diverted route are under investigation by ET. The investigation result will be presented in the next monthly EM&A report. In summary, the ET and IEC have audited the HSF movements against the SkyPier Plan and conducted follow up investigation or actions accordingly.
On the implementation of the Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for Construction and Associated Vessel (MTRMP-CAV), the upgraded Marine Surveillance System (MSS) was launched in March 2017. The MSS automatically recorded the deviation case such as speeding, entering no entry zone, not traveling through the designated gate. ET conducted checking to ensure the MSS records all deviation cases accurately. Training has been provided for the concerned skippers to facilitate them in familiarising with the requirements of the MTRMP-CAV. ET reminded contractors that all vessels shall avoid entering the Brothers Marine Park, which has been designated since 30 December 2016. 3-month rolling programmes for construction vessel activities were also received from contractors.
Results of Impact Monitoring
The monitoring works for construction dust, construction noise, water quality, construction waste and CWD were conducted during the reporting period in accordance with the Manual.
No exceedance of the Action or Limit Levels in relation to construction noise, construction waste and CWD monitoring was recorded in the reporting month.
Three exceedance cases of Limit Level of 1-hour total suspended particulate (TSP) were recorded on 10 May 2017, and the corresponding investigations were conducted accordingly. The investigation findings concluded that the exceedances were likely due to the adverse ambient air quality, but not due to the Project.
The water quality monitoring results for DO, turbidity, total alkalinity, SS, and chromium obtained during the reporting period were in compliance with their corresponding Action and Limit Levels stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programme if being exceeded. For nickel, some of the testing results exceeded the relevant Action or Limit Levels, and the corresponding investigations were conducted accordingly. The investigation findings concluded that the exceedances were not due to the Project.
Summary of Upcoming Key Issues
Key activities anticipated in the next reporting period for the Project will include the following:
Advanced Works:
Contract P560 (R) Aviation Fuel Pipeline Diversion Works
● HDD works; and
● Stockpiling of excavated materials from HDD operation.
DCM Works:
Contract 3201 to 3205 DCM Works
● Laying of geotextile and sand blanket; and
● DCM works and trials.
Reclamation Works:
Contract 3206 Main Reclamation Works
● Site office establishment; and
● Laying of sand blanket.
The key environmental issues will be associated with construction dust, construction noise, water quality, construction waste management and CWD. The implementation of required mitigation measures by the contractor will be monitored by the ET.
|
|
|
|
|
Photo Shoot for Photo Identification of CWD |
Skipper Training Conducted by Contractor |
Tool Box Talk for Handling Chemical Spillage by Contractor |
Summary Table
The following table summarizes the key findings of the EM&A programme during the reporting period from 1 to 31 May 2017:
|
|
Yes |
No |
Details |
Analysis / Recommendation / Remedial Actions |
|
Exceedance of Limit Level^ |
|
ü |
No exceedance of project-related limit level was recorded. |
Nil |
|
Exceedance of Action Level^ |
|
ü |
No exceedance of project-related action level was recorded. |
Nil |
|
Complaints Received |
ü |
|
A complaint on exhaust
air emissions from construction vessels was received on 9 May 2017.
A complaint on discharges from construction vessel was received on 22 May 2017. |
The complaint investigation was carried out in accordance with the Complaint Management Plan. The investigation detail is presented in S7.8.1.
The case is currently under investigation in accordance with the Complaint Management Plan |
|
Notification of any summons and status of prosecutions |
|
ü |
No notifications of summons or prosecution were received. |
Nil |
|
Changes that affect the EM&A |
|
ü |
There were no changes to the construction works that may affect the EM&A |
Nil |
Remarks: ^Only exceedance of action/ limit level related to Project works will be highlighted.
1
Introduction
1.1
Background
On 7 November 2014, the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Report (Register No.: AEIAR-185/2014) for the “Expansion of Hong Kong International Airport into a Three-Runway System” (the Project) was approved and an Environmental Permit (EP) (Permit No.: EP-489/2014) was issued for the construction and operation of the Project.
Airport Authority Hong Kong (AAHK) commissioned Mott MacDonald Hong Kong Limited (MMHK) to undertake the role of Environmental Team (ET) for carrying out the Environmental Monitoring & Audit (EM&A) works during the construction phase of the Project in accordance with the Updated EM&A Manual (the Manual) submitted under EP Condition 3.1. The Manual is available on the Project’s dedicated website (accessible at: http://env.threerunwaysystem.com/en/index.html). AECOM Asia Company Limited (AECOM) was employed by AAHK as the Independent Environmental Checker (IEC) for the Project.
The Project covers the expansion of the existing airport into a three-runway system (3RS) with key project components comprising land formation of about 650 ha and all associated facilities and infrastructure including taxiways, aprons, aircraft stands, a passenger concourse, an expanded Terminal 2, all related airside and landside works and associated ancillary and supporting facilities. The existing submarine aviation fuel pipelines and submarine power cables also require diversion as part of the works.
Construction of the Project is to proceed in the general order of diversion of the submarine aviation fuel pipelines, diversion of the submarine power cables, land formation, and construction of infrastructure, followed by construction of superstructures.
The updated overall phasing programme of all construction works was presented in Appendix A of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No. 7 and the contract information was presented in Appendix A of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.15.
1.2
Scope of this Report
This is the 17th Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report for the Project which summarizes the key findings of the EM&A programme during the reporting period from 1 to 31 May 2017.
1.3
Project Organisation
The Project’s organization structure presented in Appendix B of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.1 remained unchanged during the reporting month. Contact details of the key personnel have been updated and is presented in Table 1.1.
Table 1.1: Contact Information of Key Personnel
|
Party |
Position |
Name |
Telephone |
|
Project Manager’s Representative (Airport Authority Hong Kong) |
Principal Manager, Environment |
Lawrence Tsui |
2183 2734 |
|
Environmental Team (ET) (Mott MacDonald Hong Kong Limited) |
Environmental Team Leader |
Terence Kong |
2828 5919 |
|
|
Deputy Environmental Team Leader |
Heidi Yu |
2828 5704 |
|
|
Deputy Environmental Team Leader |
Keith Chau |
2972 1721 |
|
Independent Environmental Checker (IEC) (AECOM Asia Company Limited) |
Independent Environmental Checker |
Jackel Law |
3922 9376
|
|
|
Deputy Independent Environmental Checker |
Joanne Tsoi |
3922 9423 |
|
Advanced Works: |
|
|
|
|
Contract P560(R) Aviation Fuel Pipeline Diversion Works (Langfang Huayuan Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Co., Ltd.) |
Project Manager
|
Wei Shih
|
2117 0566
|
|
Environmental Officer |
Lyn Lau
|
5172 6543
|
|
|
Contract 3212 11kV Submarine Cable Diversion |
Project Director |
Colman Chan |
6193 4729 |
|
Environmental Officer |
Samantha Kong |
3995 8141 |
|
|
DCM Works: |
|
|
|
|
Contract 3201 DCM (Package 1) (Penta-Ocean-China State-Dong-Ah Joint Venture) |
Project Director
|
Tsugunari Suzuki
|
9178 9689 |
|
|
Environmental Officer
|
Sze Ming Chan
|
9384 5494 |
|
Contract 3202 DCM (Package 2) (Samsung-BuildKing Joint Venture) |
Project Manager |
Ilkwon Nam
|
9643 3117 |
|
|
Environmental Officer
|
Dickson Mak
|
9525 8408 |
|
Contract 3203 DCM (Package 3) (Sambo E&C Co., Ltd) |
Project Manager
|
Seong Jae Park
|
9683 8693 |
|
|
Environmental Officer
|
Calvin Leung
|
9203 5820 |
|
Contract 3204 DCM (Package 4) (CRBC-SAMBO Joint Venture) |
Project Manager |
Kyung-Sik Yoo
|
9683 8697
|
|
|
Environmental Officer |
Kanny Cho |
9724 6254 |
|
Contract 3205 DCM (Package 5) (Bachy Soletanche - Sambo Joint Venture) |
Deputy Project Director |
Min Park |
9683 0765 |
|
|
Environmental Officer |
Margaret Chung |
9130 3696 |
|
Reclamation Works: |
|
|
|
|
Contract 3206 (ZHEC-CCCC-CDC Joint Venture) |
Project Manager |
Kim Chuan Lim
|
3693 2288 |
|
|
Environmental Officer |
Kwai Fung Wong |
3693 2252 |
1.4
Summary of
Construction Works
The key activities of the Project carried out in the reporting period included five DCM contracts, two advanced works contracts, and a reclamation contract. The DCM contracts involved DCM works and trials, site office establishment, and laying of geotextile and sand blanket. The advanced works contracts involved cable diversion associated works, and HDD works. The reclamation contract involved site office establishment and laying of sand blanket.
1.5
Summary of
EM&A Programme Requirements
The status for all environmental aspects is presented Table 1.2. The EM&A requirements remained unchanged during the reporting period and details can be referred to Table 1.2 of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No. 1.
Table 1.2: Summary of status for all environmental aspects under the Updated EM&A Manual
|
Parameters |
Status |
|
Air Quality |
|
|
Baseline Monitoring |
The baseline air quality monitoring result has been reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.4. |
|
Impact Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Noise |
|
|
Baseline Monitoring |
The baseline noise monitoring result has been reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.4. |
|
Impact Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Water Quality |
|
|
General Baseline Water Quality Monitoring for reclamation, water jetting and field joint works |
The baseline water quality monitoring result has been reported in Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.4. |
|
General Impact Water Quality Monitoring for reclamation, water jetting and field joint works |
On-going |
|
Initial Intensive Deep Cement Mixing (DCM) Water Quality Monitoring |
Completed in May 2017 and data analysis in-progress. |
|
Early/ Regular DCM Water Quality Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Waste Management |
|
|
Waste Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Land Contamination |
|
|
Supplementary Contamination Assessment Plan (CAP) |
To be submitted with the relevant construction works. |
|
Contamination Assessment Report (CAR) for Golf Course |
The CAR for Golf Course was submitted to EPD. |
|
Terrestrial Ecology |
|
|
Pre-construction Egretry Survey Plan |
The Egretry Survey Plan was submitted and approved by EPD under EP Condition 2.14. |
|
Ecological Monitoring |
Construction works on Sheung Sha Chau Island was suspended during the ardeid’s breeding season (between April and July). The ecological monitoring is therefore suspended. |
|
Marine Ecology |
|
|
Pre-Construction Phase Coral Dive Survey |
The Coral Translocation Plan was submitted and approved by EPD under EP Condition 2.12. |
|
Coral Translocation |
The coral translocation was completed. |
|
Post-Translocation Coral Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Chinese White Dolphins (CWD) |
|
|
Vessel Survey, Land-based Theodolite Tracking and Passive Acoustic Monitoring (PAM) |
|
|
Baseline Monitoring |
Baseline CWD results were reported in the CWD Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD in accordance with EP Condition 3.4. |
|
Impact Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Landscape & Visual |
|
|
Baseline Monitoring |
The baseline landscape & visual monitoring result has been reported in Baseline Monitoring Report and submitted to EPD under EP Condition 3.4. |
|
Impact Monitoring |
On-going |
|
Environmental Auditing |
|
|
Regular site inspection |
On-going |
|
Marine Mammal Watching Plan (MMWP) implementation measures |
On-going |
|
Dolphin Exclusion Zone Plan (DEZP) implementation measures |
On-going |
|
SkyPier High Speed Ferries (HSF) implementation measures |
On-going |
|
Construction and Associated Vessels Implementation measures |
On-going |
|
Complaint Hotline and Email channel |
On-going |
|
Environmental Log Book |
On-going |
Taking into account the construction works in this reporting month, impact monitoring of air quality, noise, water quality, waste management and CWD were carried out in the reporting month.
The EM&A programme also involved weekly site inspections and related auditing conducted by the ET for checking the implementation of the required environmental mitigation measures recommended in the approved EIA Report. In order to enhance environmental awareness and closely monitor the environmental performance of the contractors, environmental briefings and regular environmental management meetings were conducted.
The EM&A programme has been following the recommendations presented in the approved EIA Report and the Manual. A summary of implementation status of the environmental mitigation measures for the construction phase of the Project during the reporting period is provided in Appendix A.
2 Air Quality Monitoring
2.1
Monitoring Stations
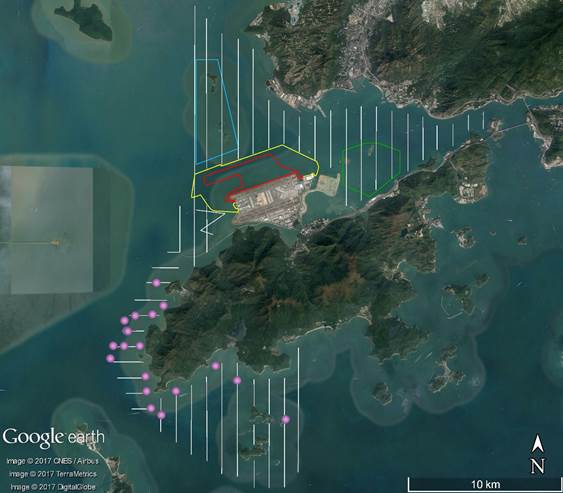
Air quality monitoring was conducted at two representative monitoring stations in the vicinity of air sensitive receivers in Tung Chung and villages in North Lantau in accordance with the Manual. Table 2.1 describes the details of the monitoring stations. Figure 2.1 shows the locations of the monitoring stations.
Table 2.1: Locations of Impact Air Quality Monitoring Stations
|
Monitoring Station |
Location |
|
AR1A |
Man Tung Road Park |
|
AR2 |
Village House at Tin Sum |
2.2
Monitoring
Requirements and Schedule
In accordance with the Manual, baseline 1-hour total suspended particulate (TSP) levels at the two air quality monitoring stations were established as presented in the Baseline Monitoring Report. Impact 1-hour TSP monitoring was conducted for three times every 6 days. The Action and Limit Levels of the air quality monitoring stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programme are provided in Table 2.2.
The air quality monitoring schedule involved in the reporting period is provided in Appendix B.
Table 2.2: Action and Limit Levels for 1-hour TSP
|
Monitoring Station |
Action Level (mg/m3) |
Limit Level (mg/m3) |
|
AR1A |
306 |
500 |
|
AR2 |
298 |
2.3
Monitoring Equipment
Portable direct reading dust meter was used to carry out the 1-hour TSP monitoring. Details of equipment are given in Table 2.3.
Table 2.3: Air Quality Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment |
Brand and Model |
Last Calibration Date |
|
Portable direct reading dust meter (Laser dust monitor) |
SIBATA LD-3B-002 (Serial No. 974350) |
26 Oct 2016 |
2.4
Monitoring
Methodology
2.4.1
Measuring Procedure
The measurement procedures involved in the impact 1-hr TSP monitoring can be summarised as follows:
a. The portable direct reading dust meter was mounted on a tripod at a height of 1.2 m above the ground.
b. Prior to the measurement, the equipment was set up for 1 minute span check and 6 second background check.
c. The one hour dust measurement was started. Site conditions and dust sources at the nearby area were recorded on a record sheet.
d. When the measurement completed, the “Count” reading per hour was recorded for result calculation.
2.4.2
Maintenance and Calibration
The portable direct reading dust meter is calibrated every year against high volume sampler (HVS) to check the validity and accuracy of the results measured by direct reading method. The
calibration certificates of the portable direct reading dust meter and calibration record of the HVS provided in Appendix B of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.11 are still valid. Any updates of calibration certificates will be reported in the Monthly EM&A report if necessary.
2.5
Analysis and
Interpretation of Monitoring Results
The monitoring results for 1-hour TSP are summarized in Table 2.4. Detailed impact monitoring results are presented in Appendix C.
Table 2.4: Summary of 1-hour TSP Monitoring Results
|
Monitoring Station |
1-hr TSP Concentration Range (mg/m3) |
Action Level (mg/m3) |
Limit Level (mg/m3) |
|
AR1A |
23 – 69 |
306 |
500 |
|
AR2 |
23 – 605 |
298 |
Three exceedance cases of Limit Level of air quality monitoring were recorded at AR2 on 10 May 2017 in the 1-hour TSP monitoring that started at 09:00am, 10:00am and 11:00am. Actions were taken accordingly based on the established Event and Action Plan as presented in the Manual. Contractors, IEC, AAHK and EPD were informed of the exceedances.
It was confirmed from the field investigation that no major construction dust emission source was observed, whilst Hong Kong was being affected by an airstream with high background pollutant concentration from the Pearl River Delta and poor atmospheric conditions for pollutant dispersion on the monitoring day. The air quality health index in Hong Kong including Tung Chung ranged from 4 (moderate) to 10+ (serious) during the monitoring period.
As confirmed with the contractors, no major dusty construction works was undertaken when the exceedances were measured. Dust suppression measures, including covering stockpiles with canvas and watering on exposed earth by P560(R) contractor, and deploying watering system for sand blanket laying by 3205 and 3206 contractors, were implemented during the monitoring period.
The exceedances of 1-hour TSP were likely due to the adverse ambient air quality, and, therefore, the exceedances were considered not due to 3RS project construction works. The mitigation measures that have been implemented were considered effective and will be implemented continuously.
General meteorological conditions throughout the impact monitoring period were recorded. Wind data including wind speed and wind direction for each monitoring day were collected from the Chek Lap Kok Wind Station.
3
Noise Monitoring
3.1
Monitoring Stations
Noise monitoring was conducted at five representative monitoring stations in the vicinity of noise sensitive receivers in Tung Chung and villages in North Lantau in accordance with the Manual. Figure 2.1 shows the locations of the monitoring stations and these are described in Table 3.1 below. As described in Section 4.3.3 of the Manual, monitoring at NM2 will commence when the future residential buildings in Tung Chung West Development become occupied.
Table 3.1: Locations of Impact Noise Monitoring Stations
|
Monitoring Station |
Location |
Type of measurement |
|
NM1A |
Man Tung Road Park |
Free field |
|
NM2(1) |
Tung Chung West Development |
To be determined |
|
NM3A |
Site Office |
Facade |
|
NM4 |
Ching Chung Hau Po Woon Primary School |
Free field |
|
NM5 |
Village House in Tin Sum |
Free field |
|
NM6 |
House No. 1, Sha Lo Wan |
Free field |
Note: (1) As described in Section 4.3.3 of the Manual, noise monitoring at NM2 will only commence after occupation of the future Tung Chung West Development.
3.2
Monitoring Requirements and Schedule
In accordance with the Manual, baseline noise levels at the noise monitoring stations were established as presented in the Baseline Monitoring Report. Impact noise monitoring was conducted once per week in the form of 30-minute measurements of Leq, L10 and L90 levels recorded at each monitoring station between 0700 and 1900 on normal weekdays. The Action and Limit Levels of the noise monitoring stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programme are provided in Table 3.2. The construction noise monitoring schedule involved in the reporting period is provided in Appendix B.
Table 3.2: Action and Limit Levels for Construction Noise
|
Monitoring Stations |
Time Period |
Action Level |
Limit Level, Leq(30mins) dB(A) |
|
NM1A, NM2, NM3A, NM4, NM5 and NM6 |
0700-1900 hours on normal weekdays |
When one documented complaint is received from any one of the sensitive receivers |
75 dB(A)(i) |
Note: (i) Reduced to 70dB(A) for school and 65dB(A) during school examination periods. No school examination took place in the reporting period.
3.3
Monitoring
Equipment
Noise monitoring was performed using sound level meter at each designated monitoring station. The sound level meters deployed comply with the International Electrotechnical Commission Publications 651:1979 (Type 1) and 804:1985 (Type 1) specifications. Acoustic calibrator was used to check the sound level meters by a known sound pressure level for field measurement. Details of equipment are given in Table 3.3.
Table 3.3: Noise Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment |
Brand and Model |
Last Calibration Date |
|
|
Integrated Sound Level Meter |
B&K 2238 (Serial No. 2800932) |
19 Jul 2016 |
|
|
B&K 2238 (Serial No. 2381580) |
8 Sep 2016 |
||
|
|
|||
|
Acoustic Calibrator |
B&K 4231 (Serial No. 3003246) |
16 May 2017 |
|
|
B&K 4231 (Serial No. 3004068) |
19 Jul 2016 |
||
3.4
Monitoring
Methodology
3.4.1
Monitoring Procedure
The monitoring procedures involved in the noise impact monitoring can be summarised as follows:
a. The sound level meter was set on a tripod at least a height of 1.2 m above the ground for free-field measurements at monitoring stations NM1A, NM4, NM5 and NM6. A correction of +3 dB(A) was applied to the free field measurements.
b. Façade measurements were made at the monitoring station NM3A.
c. Parameters such as frequency weighting, time weighting and measurement time were set.
d. Prior to and after each noise measurement, the meter was calibrated using the acoustic calibrator. If the difference in the calibration level before and after measurement was more than 1 dB(A), the measurement would be considered invalid and repeat of noise measurement would be required after re-calibration or repair of the equipment.
e. During the monitoring period, Leq, L10 and L90 were recorded. In addition, site conditions and noise sources were recorded on a record sheet.
f. Noise measurement results were corrected with reference to the baseline monitoring levels.
g. Observations were recorded when high intrusive noise (e.g. dog barking, helicopter noise) was observed during the monitoring.
3.4.2
Maintenance and Calibration
The maintenance and calibration procedures are summarised below:
a. The microphone head of the sound level meter was cleaned with soft cloth at regular intervals.
b. The meter and calibrator were sent to the supplier or laboratory accredited under Hong Kong Laboratory Accreditation Scheme (HOKLAS) to check and calibrate at yearly intervals.
Calibration certificates of the sound level meters and acoustic calibrators used in the noise monitoring provided in Appendix B of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.8 & 9 are still valid. The acoustic calibrator calibrated in May 2017 is provided in Appendix D.
3.5
Analysis and Interpretation of Monitoring Results
The construction noise monitoring results are summarized in Table 3.4 and the detailed monitoring data are provided in Appendix C.
Table 3.4: Summary of Construction Noise Monitoring Results
|
Monitoring Station |
Noise Level Range, dB(A) Leq (30 mins) |
Limit Level, dB(A) Leq (30 mins) |
|
NM1A(i) |
71 – 73 |
75 |
|
NM3A |
60 – 63 |
75 |
|
NM4(i) |
65 – 68 |
70(ii) |
|
NM5(i) |
53 – 64 |
75 |
|
NM6(i) |
64 – 70 |
75 |
Note: (i) +3 dB(A) Façade correction included;
(ii) Reduced to 65 dB(A) during school examination periods at NM4. No school examination took place in the reporting period.
As the construction activities were far away from the monitoring stations, major sources of noise dominating the monitoring stations observed during the construction noise impact monitoring were road traffic noise at NM1A, aircraft and helicopter noise at NM3A, road traffic, student activity noise, and noise from Tung Chung Sewage Pumping Station at NM4, helicopter noise at NM5, and aircraft, helicopter, and marine vessel noise at NM6 in this reporting month.
No exceedance of the Action/ Limit Level was recorded at all monitoring stations in the reporting period.
4 Water Quality Monitoring
4.1
Monitoring Stations
Water quality monitoring was conducted at a total of 23 water quality monitoring stations, comprising 12 impact stations, one mobile impact station, seven sensitive receiver stations and three control stations in the vicinity of water quality sensitive receivers around the airport island in accordance with the Manual. Table 4.1 describes the details of the monitoring stations. Figure 3.1 shows the locations of the monitoring stations.
Table 4.1: Monitoring Locations and Parameters for Impact Water Quality Monitoring
|
Monitoring Stations |
Description |
Coordinates |
Parameters |
|
|
Easting |
Northing |
|||
|
C1 |
Control |
804247 |
815620 |
DO, pH, Temperature, Salinity, Turbidity, SS, Total Alkalinity, Heavy Metals(2) |
|
C2 |
Control |
806945 |
825682 |
|
|
C3(3) |
Control |
817803 |
822109 |
|
|
IM1 |
Impact |
806458 |
818351 |
|
|
IM2 |
Impact |
806193 |
818852 |
|
|
IM3 |
Impact |
806019 |
819411 |
|
|
IM4 |
Impact |
805039 |
819570 |
|
|
IM5 |
Impact |
804924 |
820564 |
|
|
IM6 |
Impact |
805828 |
821060 |
|
|
IM7 |
Impact |
806835 |
821349 |
|
|
IM8 |
Impact |
807838 |
821695 |
|
|
IM9 |
Impact |
808811 |
822094 |
|
|
IM10 |
Impact |
809838 |
822240 |
|
|
IM11 |
Impact |
810545 |
821501 |
|
|
IM12 |
Impact |
811519 |
821162 |
|
|
IM13 |
Impact (for submarine 11 kV cable diversion) |
Mobile station (500 m envelope of water jetting works) |
DO, pH, Temperature, Salinity, Turbidity, SS |
|
|
SR1(1) |
Future Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge Hong Kong Boundary Crossing Facilities (HKBCF) Seawater Intake for cooling |
812586 |
820069 |
DO, pH, Temperature, Salinity, Turbidity, SS
|
|
SR2(3) |
Planned marine park / hard corals at The Brothers / Tai Mo To |
814166 |
821463 |
|
|
SR3 |
Sha Chau and Lung Kwu Chau Marine Park / fishing and spawning grounds in North Lantau |
807571 |
822147 |
|
|
SR4A |
Sha Lo Wan |
807810 |
817189 |
|
|
SR5A |
San Tau Beach SSSI |
810696 |
816593 |
|
|
SR6 |
Tai Ho Bay, Near Tai Ho Stream SSSI |
814663 |
817899 |
|
|
SR7 |
Ma Wan Fish Culture Zone (FCZ) |
823742 |
823636 |
|
|
SR8 |
Seawater Intake for cooling at Hong Kong International Airport (East) |
811593 |
820417 |
|
Notes:
(1) The seawater intakes of SR1 for the future HKBCF is not yet in operation, hence no water quality impact monitoring was conducted at this station. The future permanent location for SR1 during impact monitoring is subject to finalisation after the HKBCF seawater is commissioned.
(2) Details of selection criteria for the two heavy metals for early regular DCM monitoring refer to the Detailed Plan on Deep Cement Mixing available on the dedicated 3RS website http://env.threerunwaysystem.com/en/ep-submissions.html). DCM specific water quality monitoring parameters (total alkalinity and heavy metals) were only conducted at C1 to C3, SR2, and IM1 to IM12 .
(3) According to the Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Report, C3 station is not adequately representative as a control station of impact/ SR stations during the flood tide. The control reference has been changed from C3 to SR2 from 1 September 2016 onwards.
4.2
Monitoring Requirements and Schedule
General water quality monitoring and early regular DCM water quality monitoring were conducted three days per week, at mid-flood and mid-ebb tides, at the 23 water quality monitoring stations during the reporting period. The sea conditions varied from calm to rough, and the weather conditions varied from sunny to rainy during the monitoring period.
As confirmed by Contract 3212, the 11kv submarine cable diversion and associated works were conducted from 8 to 19, and 21 to 23 May 2017. The cable diversion and associated works were substantially completed on 23 May 2017. Therefore, general water quality monitoring at IM13 was ceased after 23 May 2017.
The water quality monitoring schedule for the reporting period is provided in Appendix B.
4.2.1
Action and Limit Levels for Water Quality Monitoring
The Action and Limit Levels for general water quality monitoring and regular DCM monitoring stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programme are presented in Table 4.2. The control and impact stations during flood tide and ebb tide for general water quality monitoring and regular DCM monitoring are presented in Table 4.3.
Table 4.2: Action and Limit Levels for General Water Quality Monitoring and Regular DCM Monitoring
|
Parameters |
Action Level (AL) |
Limit Level (LL) |
||
|
Action and Limit Levels for general water quality monitoring and regular DCM monitoring (excluding SR1& SR8) |
||||
|
DO in mg/L (Surface, Middle & Bottom) |
Surface and Middle 4.5 mg/L |
Surface and Middle 4.1 mg/L 5 mg/L for Fish Culture Zone (SR7) only |
||
|
Bottom 3.4 mg/L |
Bottom 2.7 mg/L |
|||
|
Suspended Solids (SS) in mg/L |
23 |
or 120% of upstream control station at the same tide of the same day, whichever is higher |
37 |
or 130% of upstream control station at the same tide of the same day, whichever is higher |
|
Turbidity in NTU |
22.6 |
36.1 |
||
|
Total Alkalinity in ppm |
95 |
99 |
||
|
Representative Heavy Metals for early regular DCM monitoring (Chromium) |
0.2 |
0.2 |
||
|
Representative Heavy Metals for early regular DCM monitoring (Nickel) |
3.2 |
|
3.6 |
|
|
Action and Limit Levels SR1 |
|
|
|
|
|
SS (mg/l) |
To be determined prior to its commissioning |
To be determined prior to its commissioning |
||
|
Action and Limit Levels SR8 |
|
|
|
|
|
SS (mg/l) |
52 |
|
60 |
|
Notes:
(1) For DO measurement, non-compliance occurs when monitoring result is lower than the limits.
(2) For parameters other than DO, non-compliance of water quality results when monitoring results is higher than the limits.
(3) Depth-averaged results are used unless specified otherwise.
(4) Details of selection criteria for the two heavy metals for early regular DCM monitoring refer to the Detailed Plan on Deep Cement Mixing available on the dedicated 3RS website http://env.threerunwaysystem.com/en/ep-submissions.html)
(5) The action and limit levels for the two representative heavy metals chosen will be the same as that for the intensive DCM monitoring.
Table 4.3: The Control and Impact Stations during Flood Tide and Ebb Tide for General Water Quality Monitoring and Regular DCM Monitoring
|
Control Station |
Impact Stations |
|
Flood Tide |
|
|
C1 |
IM1, IM2, IM3, IM4, IM5, IM6, IM7, IM8, IM13, SR3 |
|
SR2^1 |
IM7, IM8, IM9, IM10, IM11, IM12, SR1A, SR3, SR4A, SR5A, SR6, SR8 |
|
Ebb Tide |
|
|
C1 |
SR4A, SR5A, SR6 |
|
C2 |
IM1, IM2, IM3, IM4, IM5, IM6, IM7, IM8, IM9, IM10, IM11, IM12, IM13, SR1A, SR2, SR3, SR7, SR8 |
^1 As per findings of Baseline Water Quality Monitoring Report, the control reference has been changed from C3 to SR2 from 1 Sep 2016 onwards.
4.3
Monitoring Equipment
Table 4.4 summarises the equipment used for monitoring of specific water quality parameters under the impact water quality monitoring programme.
Table 4.4: Water Quality Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment |
Brand and Model |
Last Calibration Date |
|
Multifunctional Meter (measurement of DO, pH, temperature, salinity and turbidity) |
YSI ProDSS (serial no. 16J101715) |
16 Mar 2017 |
|
YSI ProDSS (serial no. 16J101716) |
16 Mar 2017 |
|
|
YSI 6920 V2 (serial no. 0001C6B0) |
16 Mar 2017 |
|
|
YSI 6920 V2 (serial no. 000109DF) |
16 Mar 2017 |
|
|
Digital Titrator (measurement of total alkalinity) |
Titrette Digital Burette 50ml Class A (serial no.10N64701) |
17 Mar 2017 |
Other equipment used as part of the impact water quality monitoring programme are listed in Table 4.5.
Table 4.5: Other Monitoring Equipment
|
Equipment |
Brand and Model |
|
Water Sampler |
Van Dorn Water Sampler |
|
Positioning Device (measurement of GPS) |
Garmin eTrex Vista HCx |
|
Current Meter (measurement of current speed and direction, and water depth) |
Sontek HydroSurveyor |
4.4
Monitoring
Methodology
4.4.1
Measuring Procedure
Water quality monitoring samples were taken at three depths (at 1m below surface, at mid-depth, and at 1m above bottom) for locations with water depth >6m. For locations with water depth between 3m and 6m, water samples were taken at two depths (surface and bottom). For locations with water depth <3m, only the mid-depth was taken. Duplicate water samples were taken and analysed.
The water samples for all monitoring parameters were collected, stored, preserved and analysed according to the Standard Methods, APHA 22nd ed. and/or other methods as agreed by the EPD. In-situ measurements at monitoring locations including temperature, pH, DO, turbidity, salinity and water depth were collected by equipment listed in Table 4.4 and Table 4.5. Water samples for heavy metals and SS analysis were stored in high density polythene bottles with no preservative added, packed in ice (cooled to 4 ºC without being frozen), delivered to the laboratory within 24 hours of collection.
4.4.2
Maintenance and Calibration
Calibration of In-situ Instruments
Wet bulb calibration for a DO meter was carried out before commencement of monitoring and after completion of all measurements each day. Calibration was not conducted at each monitoring location as daily calibration is adequate for the type of DO meter employed. A zero check in distilled water was performed with the turbidity probe at least once per monitoring day. The probe was then calibrated with a solution of known NTU. In addition, the turbidity probe was calibrated at least twice per month to establish the relationship between turbidity readings (in NTU) and levels of suspended solids (in mg/L). Accuracy check of the digital titrator was performed at least once per monitoring day.
Calibration certificates of the monitoring equipment used in the monitoring period provided in Appendix D of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.16 are still valid. Any updates of calibration certificates will be reported in the Monthly EM&A report if necessary.
4.4.3
Laboratory
Measurement / Analysis
Analysis of SS and heavy metals have been carried out by a HOKLAS accredited laboratory, ALS Technichem (HK) Pty Ltd (Reg. No. HOKLAS 066). Sufficient water samples were collected at all the monitoring stations for carrying out the laboratory SS and heavy metals determination. The SS and heavy metals determination works were started within 24 hours after collection of the water samples. The analysis of SS and heavy metals have followed the standard methods summarised in Table 4.6. The QA/QC procedures for laboratory measurement/ analysis of SS and heavy metals were presented in Appendix F of the Construction Phase Monthly EM&A Report No.8.
Table 4.6: Laboratory Measurement/ Analysis of SS and Heavy Metals
|
Parameters |
Instrumentation |
Analytical Method |
Reporting Limit |
|
Suspended Solid (SS) |
Analytical Balance |
APHA 2540D |
2 mg/L |
|
Heavy Metals |
|
|
|
|
Chromium (Cr) |
ICP-MS |
USEPA 6020A |
0.2 µg/L |
|
Nickel (Ni) |
ICP-MS |
USEPA 6020A |
0.2 µg/L |
4.5
Analysis and Interpretation of Monitoring Results
4.5.1 Summary of Monitoring
Results
The water quality monitoring results for DO, turbidity, total alkalinity, SS, and chromium obtained during the reporting period were in compliance with their corresponding Action and Limit Levels stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programme if being exceeded. For nickel, some of the testing results exceeded the relevant Action or Limit Levels, and the corresponding investigation were conducted accordingly. Details of the exceedances are presented in Section 4.5.2.
4.5.2
Summary of Findings for Investigation of Exceedances
During the reporting period, water quality monitoring was conducted at 12 impact (IM) stations, one mobile IM station, seven sensitive receiver (SR) stations, and three control stations in accordance with the Manual. The purpose of water quality monitoring at the IM stations is to promptly capture any potential water quality impact from the Project before it could become apparent at sensitive receivers (represented by the SR stations).
During the monitoring period, testing results exceeding the corresponding Action or Limit Levels were recorded on four monitoring days. Details of the exceedance cases are presented below.
Findings for Nickel Exceedance (Mid-Ebb Tide)
Table 4.7 presents a summary of the nickel compliance status at IM stations during mid-ebb tide for the reporting month.
Table 4.7: Summary of Nickel Compliance Status at IM Stations (Mid-Ebb Tide)
|
Date |
IM1 |
IM2 |
IM3 |
IM4 |
IM5 |
IM6 |
IM7 |
IM8 |
IM9 |
IM10 |
IM11 |
IM12 |
|
02/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
06/05/2017 |
|
|||||||||||
|
09/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
11/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
13/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
16/05/2017 |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
18/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
20/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
23/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
25/05/2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27/05/2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30/05/2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No. of Nickel Exceedances |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Note: Detailed results are presented in Appendix C.
Legend:
|
|
No exceedance of Action Level and Limit Level |
|
|
Exceedance of Action Level recorded at monitoring station located downstream of the 3RS Project based on dominant tidal flow |
|
|
Exceedance of Action Level recorded at monitoring station located upstream of the 3RS Project based on dominant tidal flow |
|
|
Upstream station with respect to 3RS Project during the respective tide based on dominant tidal flow |
An exceedance of Action Level was recorded on one monitoring day. However, the exceedance occurred at a monitoring station which was located upstream of the Project during ebb tide would unlikely be affected by the Project.
Findings for Nickel Exceedances (Mid-Flood Tide)
Table 4.8 presents a summary of the nickel compliance status at IM stations during mid-flood tide for the reporting month.
Table 4.8: Summary of Nickel Compliance Status at IM Stations (Mid-Flood Tide)
|
Date |
IM1 |
IM2 |
IM3 |
IM4 |
IM5 |
IM6 |
IM7 |
IM8 |
IM9 |
IM10 |
IM11 |
IM12 |
|
02/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
06/05/2017 |
|
|||||||||||
|
09/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
11/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
13/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
16/05/2017 |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
18/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
20/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
23/05/2017 |
||||||||||||
|
25/05/2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
27/05/2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
30/05/2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No. of Nickel Exceedances |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
Note: Detailed results are presented in Appendix C.
Legend:
|
|
No exceedance of Action Level and Limit Level |
|
|
Exceedance of Action Level recorded at monitoring station located downstream of the 3RS Project based on dominant tidal flow |
|
|
Exceedance of Action Level recorded at monitoring station located upstream of the 3RS Project based on dominant tidal flow |
|
|
Exceedance of Limit Level recorded at monitoring station located downstream of the 3RS Project based on dominant tidal flow |
|
|
Exceedance of Limit Level recorded at monitoring station located upstream of the 3RS Project based on dominant tidal flow |
|
|
Upstream station with respect to 3RS Project during the respective tide based on dominant tidal flow |
Exceedances of Action or Limit Levels were recorded on three monitoring days. As the exceedances occurred at stations located downstream of the Project during flood tide, which might be affected by the Project’s construction activities, exceedance investigation was carried out.
As part of the investigation on the downstream exceedance events, details of the Project’s marine construction activities on these monitoring days were collected, as well as any observations during the monitoring. The findings are summarised in Table 4.9.
Table 4.9: Summary of Findings from Investigations of Nickel Exceedances during Mid-Flood Tide
|
Date |
Marine construction works nearby |
Approximate distance from marine construction works* |
Status of water quality measures (if applicable) |
Construction vessels in the vicinity |
Turbidity / Silt plume observed near the monitoring station |
Exceedance due to Project |
|
09/05/2017 |
DCM works |
Around 500m |
Silt curtain deployed |
No |
No |
No |
|
18/05/2017 |
DCM works |
Around 500m |
Silt curtain deployed |
No |
No |
No |
|
25/05/2017 |
DCM works |
Around 500m |
Silt curtain deployed |
No |
No |
No |
According to the investigation findings, it was confirmed that DCM activities were operating normally and silt curtains were deployed for DCM works as additional measures and the silt curtains were maintained properly.
For the exceedances at IM6 to IM10 on 9 May 2017, it is noted that no SS exceedance was recorded in the same tide and the concentration (5- 6 mg/L) was well below the Action and Limit Levels. Nickel is a representative heavy metal that indicates the potential for release of contaminants from Contaminated Mud Pits (CMPs) due to the disturbance of marine sediment within CMP by DCM activities. Elevated nickel concentrations due to these activities should be associated with similar elevated SS levels. However, the low SS levels at impact stations indicates that the active DCM works have limited or insignificant effect on downstream water quality. Based on these findings, the exceedances were considered not due to the Project and may be due to natural fluctuation or other sources not related to the Project.
For the exceedances at IM7 on 18 May 2017 and IM8 on 25 May 2017, the exceedances appeared to be isolated cases with no observable temporal and spatial trend to indicate any effect due to Project activities. Furthermore, no exceedance was recorded at other downstream monitoring stations, including IM8 on 18 May 2017 and IM7 on 25 May 2017, which were similarly close to active DCM works during the same monitoring period. Based on these findings, the exceedances were considered not due to the Project.
Conclusions
Based on the findings of the exceedance investigations, it is concluded that the exceedances were not due to the Project. Hence no SR was adversely affected by the Project. All required actions under the Event and Action Plan were followed. Exceedances appeared to be due to natural fluctuation or other sources not related to the Project.
Nevertheless, recognising that the IM stations represent a ‘first line of defence’, the non-project related exceedances identified at IM stations were attended to as a precautionary measure. As part of the EM&A programme, the construction methods and mitigation measures for water quality will continue to be monitored and opportunities for further enhancement will continue to be explored and implemented where possible, to strive for better protection of water quality and the marine environment.
In the meantime, the contractors were reminded to implement and maintain all mitigation measures during weekly site inspection and regular environmental management meetings. These include maintaining mitigation measures for DCM works and sand blanket laying works properly as recommended in the Manual.
5
Waste Management
5.1
Monitoring Requirements
In accordance with the Manual, the waste generated from construction activities was audited once per week to determine if wastes are being managed in accordance with the Waste Management Plan (WMP) prepared for the Project, contract-specific WMP, and any statutory and contractual requirements. All aspects of waste management including waste generation, storage, transportation and disposal were assessed during the audits. The Action and Limit levels of the construction waste are provided in Table 5.1.
Table 5.1: Action and Limit Levels for Construction Waste
|
Monitoring Stations |
Action Level |
Limit Level |
|
Construction Area |
When one valid documented complaint is received |
Non-compliance of the WMP, contract-specific WMPs, any statutory and contractual requirements |
5.2
Waste Management Status
Weekly monitoring on all works contracts were carried out by the ET to check and monitor the implementation of proper waste management practices during the construction phase.
Recommendations including provision and maintenance of spill kits and drip trays, provision of proper storage area for general refuse, chemical and chemical waste; and segregation of recyclables from general refuse. The contractors had taken actions to implement the recommended measures.
Based on the Contractor’s information, about 1071m3 of excavated materials were produced from the HDD launching site under P560(R) in the reporting period. The generated excavated materials were temporarily stored at the stockpiling area. The excavated material will be reused in the Project.
Based on the updated information, around 82 tonnes of general refuse was disposed of to the WENT Landfill by the advanced works contract and DCM contracts in April 2017.
In addition, metal was recycled during the reporting month. Around 83 tonnes of general refuse was disposed of to the WENT Landfill and 0.08 tonnes of chemical waste was disposed of to the Tsing Yi Chemical Waste Treatment by the advanced works contract and DCM contracts in May 2017. Around 615m3 of Construction and Demolition (C&D) material generated from the DCM contract for site office establishment was disposed of as public fill.
No exceedances of the Action or Limit Levels were recorded in the reporting period.
6 Chinese White Dolphin Monitoring
6.1
CWD
Monitoring Requirements
In accordance with the Manual, Chinese White Dolphin (CWD) monitoring by small vessel line-transect survey supplemented by land-based theodolite tracking and passive acoustic monitoring should be conducted during construction phase.
The small vessel line-transect survey as proposed in the Manual should be conducted at a frequency of two full survey per month while land-based theodolite tracking should be conducted at a frequency of one day per month per station during the construction phase. In addition to the land-based theodolite tracking required for impact monitoring as stipulated in the Manual, supplemental theodolite tracking have also been conducted during the implementation for the SkyPier HSF diversion and speed control in order to assist in monitoring the effectiveness of these measures, i.e. in total twice per month at the Sha Chau station and three times per month at the Lung Kwu Chau station.
The Action Level (AL) and Limit Level (LL) for CWD monitoring were formulated by the action response approach using the running quarterly dolphin encounter rates STG and ANI derived from the baseline monitoring data, as presented in the CWD Baseline Monitoring Report. The derived values of AL and LL for CWD monitoring were summarized in Table 6.1.
Table 6.1: Derived Values of Action Level (AL) and Limit Level (LL) for Chinese White Dolphin Monitoring
|
|
NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL as a Whole |
|
Action Level |
Running quarterly* STG < 1.86 & ANI < 9.35 |
|
Limit Level |
Two consecutive running quarterly^ (3-month) STG < 1.86 & ANI < 9.35 |
[Notes for Table 6.1 (referring to the baseline monitoring report):
*Action Level – running quarterly STG & ANI will be calculated from the three preceding survey months. For CWD monitoring for May 2017, data from 1 March 2017 to 31 May 2017 will be used to calculate the running quarterly encounter rates STG & ANI;
^Limit Level – two consecutive running quarters mean both the running quarterly encounter rates of the preceding month April 2017 (calculated by data from February 2017 to April 2017) and the running quarterly encounter rates of this month (calculated by data from March 2017 to May 2017).
AL and/or LL will be exceeded if both STG and ANI fall below the criteria.]
6.2
CWD
Monitoring Transects and Stations
6.2.1
Small Vessel Line-transect Survey
Small vessel line-transect surveys were conduct along the transects covering Northeast Lantau (NEL), Northwest Lantau (NWL), Airport West (AW), West Lantau (WL) and Southwest Lantau (SWL) areas as proposed in the Manual, which are consistent with the Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department (AFCD) long-term monitoring programme (except the addition of AW). The AW transect has not been previously surveyed in the AFCD programme due to the restrictions of HKIA Exclusion Zone, nevertheless, this transect was established during the EIA of the 3RS Project and refined in the Manual with the aim to collect project specific baseline information within the HKIA Approach Area to fill the data gap that was not covered by the AFCD programme. This provided a larger sample size for estimating the density, abundance and patterns of movements in the broader study area of the project.
The planned vessel survey transect lines follow the waypoints set for construction phase monitoring as proposed in the Manual and depicted in Figure 6.1 with the waypoint coordinates of all transect lines given in Table 6.2, which are subject to on-site refinement based on the actual survey conditions and constraints.
Table 6.2: Coordinates of Transect Lines in NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL Survey Areas
|
Waypoint |
Easting |
Northing |
Waypoint |
Easting |
Northing |
|
NEL |
|||||
|
1S |
813525 |
820900 |
6N |
818568 |
824433 |
|
1N |
813525 |
824657 |
7S |
819532 |
821420 |
|
2S |
814556 |
818449 |
7N |
819532 |
824209 |
|
2N |
814559 |
824768 |
8S |
820451 |
822125 |
|
3S |
815542 |
818807 |
8N |
820451 |
823671 |
|
3N |
815542 |
824882 |
9S |
821504 |
822371 |
|
4S |
816506 |
819480 |
9N |
821504 |
823761 |
|
4N |
816506 |
824859 |
10S |
822513 |
823268 |
|
5S |
817537 |
820220 |
10N |
822513 |
824321 |
|
5N |
817537 |
824613 |
11S |
823477 |
823402 |
|
6S |
818568 |
820735 |
11N |
823477 |
824613 |
|
NWL |
|||||
|
1S |
804671 |
814577 |
5S |
808504 |
821735 |
|
1N |
804671 |
831404 |
5N |
808504 |
828602 |
|
2Sb |
805475 |
815457 |
6S |
809490 |
822075 |
|
2Nb |
805476 |
818571 |
6N |
809490 |
825352 |
|
2Sa |
805476 |
820770 |
7S |
810499 |
822323 |
|
2Na |
805476 |
830562 |
7N |
810499 |
824613 |
|
3S |
806464 |
821033 |
8S |
811508 |
821839 |
|
3N |
806464 |
829598 |
8N |
811508 |
824254 |
|
4S |
807518 |
821395 |
9S |
812516 |
821356 |
|
4N |
807518 |
829230 |
9N |
812516 |
824254 |
|
AW |
|||||
|
1W |
804733 |
818205 |
2W |
805045 |
816912 |
|
1E |
806708 |
818017 |
2E |
805960 |
816633 |
|
WL |
|||||
|
1W |
800600 |
805450 |
7W |
800400 |
811450 |
|
1E |
801760 |
805450 |
7E |
802400 |
811450 |
|
2W |
800300 |
806450 |
8W |
800800 |
812450 |
|
2E |
801750 |
806450 |
8E |
802900 |
812450 |
|
3W |
799600 |
807450 |
9W |
801500 |
813550 |
|
3E |
801500 |
807450 |
9E |
803120 |
813550 |
|
4W |
799400 |
808450 |
10W |
801880 |
814500 |
|
4E |
801430 |
808450 |
10E |
803700 |
814500 |
|
5W |
799500 |
809450 |
11W |
802860 |
815500 |
|
5E |
801300 |
809450 |
12S/11E |
803750 |
815500 |
|
6W |
799800 |
810450 |
12N |
803750 |
818500 |
|
6E |
801400 |
810450 |
|
|
|
|
SWL |
|||||
|
1S |
802494 |
803961 |
6S |
807467 |
801137 |
|
1N |
802494 |
806174 |
6N |
807467 |
808458 |
|
2S |
803489 |
803280 |
7S |
808553 |
800329 |
|
2N |
803489 |
806720 |
7N |
808553 |
807377 |
|
3S |
804484 |
802509 |
8S |
809547 |
800338 |
|
3N |
804484 |
807048 |
8N |
809547 |
807396 |
|
4S |
805478 |
802105 |
9S |
810542 |
800423 |
|
4N |
805478 |
807556 |
9N |
810542 |
807462 |
|
5S |
806473 |
801250 |
10S |
811446 |
801335 |
|
5N |
806473 |
808458 |
10N |
811446 |
809436 |
6.2.2
Land-based Theodolite Tracking
Land-based theodolite tracking stations were set up at two locations, one facing east/south/west on the southern slopes of Sha Chau (SC), and the other facing north/northeast/northwest at Lung Kwu Chau (LKC). The stations (D and E) are depicted in Figure 6.2 and shown in Table 6.3 with position coordinates, height of station and approximate distance of consistent theodolite tracking capabilities for CWD.
Table 6.3: Land-based Survey Station Details
|
Stations |
Location |
Geographical Coordinates |
Station Height (m) |
Approximate Tracking Distance (km) |
|
D |
Sha Chau (SC) |
22° 20’ 43.5” N 113° 53’ 24.66” E |
45.66 |
2 |
|
E |
Lung Kwu Chau (LKC) |
22° 22’ 44.83” N 113° 53’ 0.2” E |
70.40 |
3 |
6.3
CWD
Monitoring Methodology
6.3.1
Small Vessel Line-transect Survey
Small vessel line-transect surveys provided data for density and abundance estimation and other assessments using distance-sampling methodologies, specifically, line-transect methods.
The surveys involved small vessel line-transect data collection and have been designed to be similar to, and consistent with, previous surveys for the AFCD for their long-term monitoring of small cetaceans in Hong Kong. The survey was designed to provide systematic, quantitative measurements of density, abundance and habitat use.
As mentioned in Section 6.2.1, the transects covered NEL, NWL covering the AW, WL and SWL areas as proposed in the Manual and are consistent with the AFCD long-term monitoring programme (except AW). There are two types of transect lines:
● Primary transect lines: the parallel and zigzag transect lines as shown in Figure 6.1; and
● Secondary transect lines: transect lines connecting between the primary transect lines and crossing islands.
All data collected on both primary and secondary transect lines were used for analysis of sighting distribution, group size, activities including association with fishing boat, and mother-calf pair. Only on-effort data collected under conditions of Beaufort 0-3 and visibility of approximately 1200 m or beyond were used for analysis of the CWD encounter rates.
A 15-20 m vessel with a flying bridge observation platform about 4 to 5 m above water level and unobstructed forward view, and a team of three to four observers were deployed to undertake the surveys. Two observers were on search effort at all times when following the transect lines with a constant speed of 7 to 8 knots (i.e. 13 to 15 km per hour), one using 7X handheld binoculars and the other using unaided eyes and recording data.
During on-effort survey periods, the survey team recorded effort data including time, position (waypoints), weather conditions (Beaufort sea state and visibility) and distance travelled in each series with assistance of a handheld GPS device. The GPS device also continuously and automatically logged data including time, position (Latitude and longitude) and vessel speed throughout the entire survey.
When CWDs were seen, the survey team was taken off-effort, the dolphins were approached and photographed for photo-ID information (using a Canon 7D [or similar] camera and long 300 mm+ telephoto lens), then followed until they left the study area or were lost. At that point, the boat returned (off effort) to the next survey line and began to survey on effort again.
Focal follows of dolphins were conducted where practicable (i.e. when individual dolphins or small stable groups of dolphins with at least one member that could be readily identifiable with unaided eyes during observations and weather conditions are favourable). These involved the boat following (at an appropriate distance to minimize disturbance) an identifiable individual dolphin for an extended period of time, and collecting detailed data on its location, behaviour, response to vessels, and associates.
6.3.2
Photo Identification
CWDs can be identified by their unique features like presence of scratches, nick marks, cuts, wounds, deformities of their dorsal fin and distinguished colouration and spotting patterns.
When CWDs were observed, the survey team was taken off-effort, the dolphins were approached and photographed for photo-ID information (using a Canon 7D [or similar] camera and long 300 mm+ telephoto lens). The survey team attempted to photo both sides of every single dolphin in the group as the colouration and spotting pattern on both sides may not be identical. The photos were taken at the highest available resolution and stored on Compact Flash memory cards for transferring into a computer.
All photos taken were initially examined to sort out those containing potentially identifiable individuals. These sorted-out images would then be examined in detail and compared to the CWD photo-identification catalogue established for 3RS during the baseline monitoring stage.
6.3.3
Land-based Theodolite Tracking
Land-based monitoring obtains fine-scale information on the
time of day and movement patterns of the CWDs. A digital theodolite
(Sokkia/Sokkisha Model DT5 or similar equipment) with
30-power magnification and 5-s precision was used to obtain the vertical and horizontal angle of each
dolphin and vessel position. Angles
were converted to geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) and
data were recorded using Pythagoras software, Version 1.2. This
method delivers precise positions of multiple
spatially distant targets in a short period of time. The
technique is fully non-invasive, and allows for time and cost-effective
descriptions of dolphin habitat use patterns at all times of daylight.
Three surveyors (one theodolite operator, one computer operator, and one observer) were involved in each survey. Observers searched for dolphins using unaided eyes and handheld binoculars (7X50). Theodolite tracking sessions were initiated whenever an individual CWD or group of CWDs was located. Where possible, a distinguishable individual was selected, based on colouration, within the group. The focal individual was then continuously tracked via the theodolite, with a position recorded each time the dolphin surfaced. In case an individual could not be positively distinguished from other members, the group was tracked by recording positions based on a central point within the group whenever the CWD surfaced. Tracking continued until animals were lost from view; moved beyond the range of reliable visibility (>1-3 km, depending on station height); or environmental conditions obstructed visibility (e.g., intense haze, Beaufort sea state >4, or sunset), at which time the research effort was terminated. In addition to the tracking of CWD, all vessels that moved within 2-3 km of the station were tracked, with effort made to obtain at least two positions for each vessel.
Theodolite tracking included focal follows of CWD groups and vessels. Priority was given to tracking individual or groups of CWD. The survey team also attempted to track all vessels moving within 1 km of the focal CWD.
6.4
Monitoring
Results and Observations
6.4.1
Small Vessel Line-transect Survey
Survey Effort
Within this reporting month, two complete sets of small vessel line-transect surveys were conducted on the 4th, 5th, 8th, 9th, 11th, 17th, 22nd and 23rd May 2017, covering all transects in NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL survey areas for twice.
A total of 449.00 km of survey effort was collected from these surveys, with around 89.99% of the total survey effort being conducted under favourable weather condition (i.e. Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility). Details of the survey effort are given in Appendix C.
Sighting Distribution
In May 2017, 19 groups of CWDs with 111 individuals were sighted. Amongst these sightings, 17 groups of CWDs with 103 animals were recorded during on-effort search under favourable weather conditions (i.e. Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility). Details of cetacean sightings are presented in Appendix C.
Distribution of all CWD sightings recorded in
May 2017 is illustrated in Figure
6.3. In May 2017, CWDs were only sighted in WL and SWL, with
more sightings recorded in WL than in SWL. In WL survey area, CWD sightings
were recorded from Tai O to Fan Lau. In SWL, CWD sightings were recorded along
the coastal waters from Fan Lau to Shek Pik and also in eastern waters of Soko
Islands. No sightings of CWDs were recorded in the vicinity of or within the
3RS land-formation footprint.
Figure 6.3: Sightings Distribution of Chinese White Dolphins
[Pink circle: Sighting locations of CWD, White line: Vessel survey transects, Blue polygon: Sha Chau and Lung Kwu Chau Marine Park (SCLKCMP), Green polygon: Brothers Marine Park (BMP) Red polygon: 3RS land-formation footprint, Yellow line: 3RS temporary works area boundary]
Encounter Rate
Two types of dolphin encounter rates were calculated based on the data from May 2017. They included the number of dolphin sightings per 100 km survey effort (STG) and total number of dolphins per 100 km survey effort (ANI) in the whole survey area (i.e. NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL). In the calculation of dolphin encounter rates, only survey data collected under favourable weather condition (i.e. Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility) were used. The formulae used for calculation of the encounter rates are shown below:
Encounter
Rate by Number of Dolphin Sightings (STG)
![]()
Encounter
Rate by Number of Dolphins (ANI)
![]()
(Notes: Only data collected under Beaufort 3 or below condition was used)
In May 2017, a total of 404.06 km of survey effort were conducted under Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility, whilst a total number of 17 on-effort sightings with a total number of 103 dolphins from on-effort sightings were obtained under such condition. Calculation of the encounter rates in May 2017 are shown in Appendix C.
For the running quarter of the reporting month (i.e., from March 2017 to May 2017), a total of 1210.64 km of survey effort were conducted under Beaufort Sea State 3 or below with favourable visibility, whilst a total number of 37 on-effort sightings and a total number of 175 dolphins from on-effort sightings were obtained under such condition. Calculation of the running quarterly encounter rates are shown in Appendix C.
The STG and ANI of CWD in the whole survey area (i.e. NEL, NWL, AW, WL and SWL) during the month of May 2017 and during the running quarter are presented in Table 6.4 below and compared with the Action Level. The running quarterly encounter rates STG and ANI did not trigger the Action Level (i.e., remained above the Action Level).
Table 6.4: Comparison of CWD Encounter Rates of the Whole Survey Area with Action Levels
|
|
Encounter Rate (STG) |
Encounter Rate (ANI) |
|
May 2017 |
4.21 |
25.49 |
|
Running Quarter from March 2017 to May 2017* |
3.06 |
14.46 |
|
Action Level |
Running quarterly* < 1.86 |
Running quarterly* < 9.35 |
*Running quarterly encounter rates STG & ANI were calculated from data collected in the reporting month and the two preceding survey months, i.e. the data from March 2017 to May 2017, containing six sets of transect surveys for all monitoring areas.
Group Size
In May 2017, 19 groups of CWDs with 111 individuals were sighted, and the average group size of CWDs was 5.84 individuals per group. The number of CWD groups with small-sized (i.e. 1-2 individuals) was five while that of medium-sized (i.e. 3-9 individuals) was 11. Three large CWD groups (i.e. 10 or more individuals) sighted in WL were recorded in this reporting month.
Activities and Association with Fishing Boats
Ten out of 19 sightings of CWDs were recorded engaging in feeding activities in May 2017, whilst none of these sightings was associated with operating fishing boat.
Mother-calf Pair
In May 2017, five sightings of CWDs were recorded with the presence of mother-and-unspotted juvenile pairs. Four out of these five sightings were recorded in WL while the remaining one was recorded in SWL.
6.4.2
Photo Identification
In May 2017, a total number of 35 different CWD individuals were identified for totally 47 times. A summary of photo identification works is presented in Table 6.5. Representative photos of these individuals are given in Appendix C.
Table 6.5: Summary of Photo Identification
|
Individual ID |
Date of Sighting (dd/mm/yyyy) |
Sighting Group No. |
Area |
|
|
Individual ID |
Date of Sighting (dd/mm/yyyy) |
Sighting Group No. |
Area |
||||
|
NLMM001 |
11/05/2017 |
3 |
WL |
|
WLMM008 |
11/05/2017 |
7 |
WL |
|
||||
|
NLMM023 |
11/05/2017 |
1 |
WL |
|
WLMM018 |
11/05/2017 |
8 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM007 |
11/05/2017 |
9 |
WL |
|
WLMM042 |
11/05/2017 |
3 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM010 |
11/05/2017 |
10 |
SWL |
|
WLMM043 |
05/05/2017 |
1 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM011 |
11/05/2017 |
11 |
SWL |
|
WLMM070 |
11/05/2017 |
11 |
SWL |
|
||||
|
SLMM015 |
04/05/2017 |
1 |
SWL |
|
WLMM073 |
11/05/2017 |
8 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM022 |
05/05/2017 |
4 |
WL |
|
WLMM076 |
05/05/2017 |
1 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
|
5 |
WL |
|
WLMM077 |
05/05/2017 |
1 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM023 |
05/05/2017 |
4 |
WL |
|
WLMM078 |
05/05/2017 |
1 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
|
5 |
WL |
|
WLMM079 |
05/05/2017 |
4 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
11/05/2017 |
3 |
WL |
|
|
|
5 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
|
8 |
WL |
|
WLMM080 |
11/05/2017 |
2 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM027 |
11/05/2017 |
3 |
WL |
|
WLMM081 |
11/05/2017 |
2 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
|
8 |
WL |
|
WLMM082 |
11/05/2017 |
2 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM028 |
05/05/2017 |
5 |
WL |
|
|
|
4 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM047 |
11/05/2017 |
8 |
WL |
|
WLMM083 |
11/05/2017 |
2 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM052 |
05/05/2017 |
4 |
WL |
|
WLMM084 |
11/05/2017 |
3 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
|
5 |
WL |
|
|
|
7 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
11/05/2017 |
10 |
SWL |
|
WLMM085 |
11/05/2017 |
4 |
WL |
|
||||
|
SLMM056 |
11/05/2017 |
11 |
SWL |
|
WLMM086 |
11/05/2017 |
5 |
WL |
|
||||
|
WLMM004 |
05/05/2017 |
4 |
WL |
|
WLMM087 |
11/05/2017 |
5 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
|
5 |
WL |
|
WLMM088 |
11/05/2017 |
8 |
WL |
|
||||
|
WLMM007 |
05/05/2017 |
1 |
WL |
|
WLMM089 |
11/05/2017 |
8 |
WL |
|
||||
|
|
11/05/2017 |
6 |
WL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
6.4.3
Land-based Theodolite Tracking
Survey Effort
Land-based theodolite tracking surveys were conducted at LKC on 19th, 25th and 29th May 2017 and at SC on 17th and 22nd May 2017, with a total of five days of land-based theodolite tracking survey effort accomplished in this reporting month. In total, two CWD groups were tracked at LKC station during the surveys. Information of survey effort and CWD groups sighted during these land-based theodolite tracking surveys are presented in Table 6.6. Details of the survey effort and CWD groups tracked are presented in Appendix C. The first sighting locations of CWD groups tracked at LKC station during land-based theodolite tracking surveys in May 2017 were depicted in Figure 6.4. No CWD group was sighted from SC station in this reporting month.
Table 6.6: Summary of Survey Effort and CWD Group of Land-based Theodolite Tracking
|
Land-based Station |
No. of Survey Sessions |
Survey Effort (hh:mm) |
No. of CWD Groups Sighted |
CWD Group Sighting per Survey Hour |
|
Lung Kwu Chau |
3 |
18:00 |
2 |
0.11 |
|
Sha Chau |
2 |
12:00 |
0 |
0 |
|
TOTAL |
5 |
30:00 |
2 |
0.07 |
Figure 6.4: Plots of First Sightings of All CWD Groups obtained from Land-based Stations
[Green triangle: LKC station; Green square: CWD group off LKC; Blue line: SCLKCMP boundary]
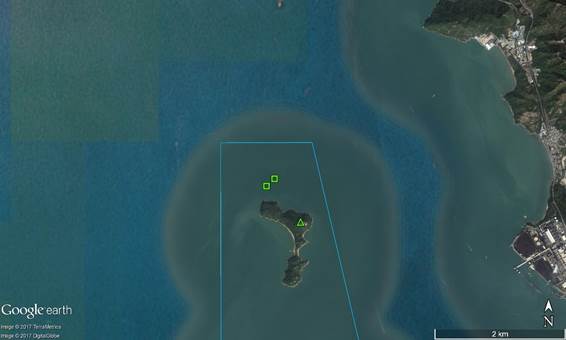
6.5
Progress Update
on Passive Acoustic Monitoring
Underwater acoustic monitoring using Passive Acoustic Monitoring (PAM) should be undertaken during land formation related construction works. In this reporting month, the Ecological Acoustic Recorder (EAR) has been retrieved and re-deployed on 13 May 2017 and positioned at south of Sha Chau Island with 20% duty cycle (Figure 6.5). The EAR deployment is generally for 4-6 weeks prior to data retrieval for analysis. Acoustic data is reviewed to give an indication of CWDs occurrence patterns and to obtain anthropogenic noise information simultaneously. Analysis (by a specialized team of acousticians) involved manually browsing through every acoustic recording and logging the occurrence of dolphin signals. All data will be re-played by computer as well as listened to by human ears for accurate assessment of dolphin group presence. As the period of data collection and analysis takes more than two months, PAM results could not be reported in monthly intervals.
6.6
Site Audit for
CWD-related Mitigation Measures
During the reporting period, silt curtains were in place by the contractors for sand blanket laying works, in which dolphin observers were deployed by each contractor in accordance with the Marine Mammal Watching Plan (MMWP). Teams of at least two dolphin observers were deployed at 10 to 12 dolphin observation stations by the contractors for continuous monitoring of the Dolphin Exclusion Zone (DEZ) by all contractors for DCM and water jetting works for submarine cable diversion in accordance with the DEZ Plan. Trainings for the proposed dolphin observers on the implementation of MMWP and DEZ monitoring were provided by the ET prior to the aforementioned works, with a cumulative total of 327 individuals being trained and the training records kept by the ET. From the contractors’ MMWP observation records and DEZ monitoring records, no dolphin or other marine mammals were observed within or around the silt curtains or the DEZs in this reporting month. These contractors’ records were also audited by the ET during site inspection.
Audits of acoustic decoupling for construction vessels were carried out during weekly site inspection and the observations are summarised in Section 7.1. Audits of SkyPier high speed ferries route diversion and speed control and construction vessel management are presented in Section 7.2 and Section 7.3 respectively.
6.7
Timing of
Reporting CWD Monitoring Results
Detailed analysis of CWD monitoring results collected by small vessel line-transect survey will be provided in future quarterly reports. Detailed analysis of CWD monitoring results collected by land-based theodolite tracking and PAM will be provided in future annual reports after a larger sample size of data has been collected.
6.8
Summary of CWD Monitoring
Monitoring of CWD was conducted with two complete sets of small vessel line-transect surveys and five days of land-based theodolite tracking survey effort as scheduled. The running quarterly encounter rates STG and ANI in the reporting month did not trigger the Action Level for CWD monitoring.
7 Environmental Site Inspection and Audit
7.1
Environmental Site Inspection
Weekly site inspections of the construction works for the advanced works contracts and DCM contracts were carried out by the ET to audit the implementation of proper environmental pollution control and mitigation measures for the Project. The weekly site inspection schedule of the construction works is provided in Appendix B. Bi-weekly site inspections were also conducted by the IEC. Observations have been recorded in the site inspection checklists and provided to the contractors together with the appropriate follow-up actions where necessary.
The key observations from site inspection and associated recommendations were related to provision and maintenance of drip trays and chemical waste storage area, as well as implementation of noise mitigation and dust suppression measures. In addition, recommendations were also provided during site inspection on barges, which included display of Non-road Mobile Machinery Label (NRMM) on generators; display of valid permits and licenses on barges; provision and maintenance of drip trays and spill kits; provision of proper storage area for general refuse, chemicals, and chemical waste; segregation of recyclables from general refuse; implementation of proper wastewater treatment, dust suppression measures, spill and runoff preventive measures, and dark smoke preventive measures; as well as proper installation and maintenance of silt curtains.
A summary of implementation status of the environmental mitigation measures for the construction phase of the Project during the reporting period is provided in Appendix A.
7.2
Audit of Route
Diversion and Speed Control of the SkyPier High Speed
Ferries
The Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for High Speed Ferries of SkyPier (the SkyPier Plan) was submitted to the Advisory Council on the Environment (ACE) for comment and subsequently submitted to and approved by EPD in November 2015 under EP Condition 2.10. The approved SkyPier Plan is available on the dedicated website of the Project. In the SkyPier Plan, AAHK has committed to implementing the mitigation measure of requiring high speed ferries (HSFs) of SkyPier travelling between HKIA and Zhuhai / Macau to start diverting the route with associated speed control across the area, i.e. Speed Control Zone (SCZ), with high CWD abundance. The route diversion and speed restriction at the SCZ have been implemented since 28 December 2015.
Key audit findings for the SkyPier HSFs travelling to/from Zhuhai and Macau against the requirements of the SkyPier Plan during the reporting period are summarized in Table 7.1. The daily movements of all SkyPier HSFs in May 2017 (i.e., 91 to 97 daily movements) were within the maximum daily cap of 125 daily movements. Status of compliance with the annual daily average of 99 movements will be further reviewed in the annual EM&A Report.
In total, 864 ferry movements between HKIA SkyPier and Zhuhai / Macau were recorded in May 2017 and the data are presented in Appendix G. The time spent by the SkyPier HSFs travelling through the SCZ in May 2017 were presented in Figure 7‑1. It will take 9.6 minutes to travel through the SCZ when the SkyPier HSFs adopt the maximum allowable speed of 15 knots within the SCZ. Figure 7‑1 shows that all of the SkyPier HSFs spent more than 9.6 minutes to travel through the SCZ.
Figure 7‑1 Duration of the SkyPier HSFs travelling through the SCZ for May 2017
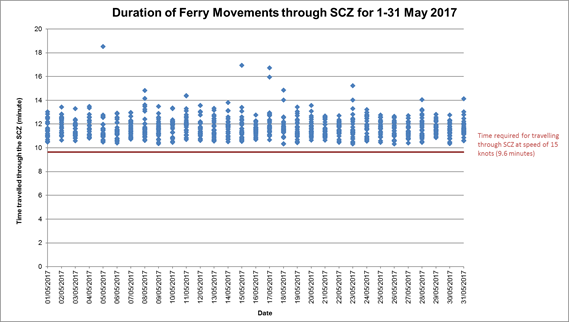
Note: Data above the red line indicated that the time spent by the SkyPier HSFs travelling through the SCZ is more than 9.6 minutes, which is in compliance with the SkyPier Plan.
Four ferries were recorded with minor deviation from the diverted route on 5, 13, 22 and 24 May 2017. Notices were sent to the ferry operator (FO) and the cases are under investigation by ET. The investigation result will be presented in the next monthly EM&A report
The cases of minor deviation from the diverted route recorded on 2, 8, 14 and 16 April 2017 were followed up after receiving information from the FO. For the cases on 2, 8 and 16 April 2017, ET’s investigation found that the vessel captain had to give way to a vessel to ensure safety. After that, the HSF had returned to the normal route following the SkyPier Plan. The remaining minor route deviation case on 14 April 2017 was due to strong tidal wave and current. After that, the HSF had returned to the normal route immediately.
Table 7.1: Summary of Key Audit Findings against the SkyPier Plan
|
Requirements in the SkyPier Plan |
1 May to 31 May 2017 |
|
Total number of ferry movements recorded and audited |
864 |
|
Use diverted route and enter / leave SCZ through Gate Access Points |
4 deviations, which are under investigation |
|
Speed control in speed control zone |
The average speeds taken within the SCZ of all HSFs were within 15 knots (7.8 knots to 14.0 knots), which complied with the SkyPier Plan. The time used by HSFs to travel through SCZ is presented in Figure 7-1. |
|
Daily Cap (including all SkyPier HSFs)
|
91 to 97 daily movements (within the maximum daily cap - 125 daily movements). |
7.3
Audit of
Construction and Associated Vessels
The updated Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for Construction and Associated Vessel (MTRMP-CAV) was submitted and approved in November 2016 by EPD under EP Condition 2.9. The approved Plan is available on the dedicated website of the Project.
ET carried out the following actions during the reporting period:
· Four skipper training sessions were held for contractors’ concerned skippers of relevant construction vessels to familiarize them with the predefined routes; general education on local cetaceans; guidelines for avoiding adverse water quality impact; the required environmental practices / measures while operating construction and associated vessels under the Project; and guidelines for operating vessels safely in the presence of CWDs. The list of all trained skippers was properly recorded and maintained by ET.
· Five skipper training sessions were held by contractor’s Environmental Officer. Competency test was subsequently conducted with the trained skippers by ET.
· 40 skippers were trained by ET and 8 skippers were trained by contractor’s Environmental Officer in May 2017. In total, 659 skippers were trained from August 2016 to May 2017.
· The upgraded Marine Surveillance System (MSS) was launched in March 2017. The MSS automatically recorded deviation cases such as speeding, entering no entry zone, not traveling through the designated gate. ET conducted checking to ensure the MSS records deviation cases accurately.
· Deviations such as speeding in the works area, entering from non-designated gates and entering no-entry zones were identified. All the concerned contractors were reminded to comply with the requirements of the MTRMP-CAV during the bi-weekly MTCC audit.
· 3-month rolling programmes (one month record and two months forecast) for construction vessel activities were received from the contractors in order to help maintain the number of construction and associated vessels on site to a practicable minimal level.
The IEC of the Project had performed audit on the compliance of the requirements as part of the EM&A programme.
7.4
Implementation of Dolphin Exclusion Zone
The DEZ Plan was submitted in accordance with EP Condition 3.1 (v) requirement and Section 10.3 of the Updated EM&A Manual, and approved in April 2016 by EPD. The 24-hour DEZs with a 250m radius for marine works were established and implemented by the contractors for DCM and water jetting works for submarine cable diversion in accordance with the DEZ Plan.
During the reporting period, ET has been notified that no dolphins were sighted within the DEZ by the contractors. ET has checked the relevant records to audit the implementation of DEZ and followed up with contractors on improper practices in DEZ monitoring identified during site inspection.
7.5
Ecological
Monitoring
In accordance with the Manual, ecological monitoring shall be undertaken monthly at the Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) daylighting location on Sheung Sha Chau Island during the HDD construction works period from August to March. Since the construction works on Sheung Sha Chau is suspended during the ardeid’s breeding season between April to July, no ecological monitoring was carried out in this reporting period.
7.6
Status of
Submissions under Environmental Permits
The current status of submissions under the EP up to the reporting period is presented in Table 7.2.
Table 7.2: Status of Submissions under Environmental Permit
|
EP Condition |
Submission |
Status |
|
2.1 |
Complaint Management Plan |
Accepted / approved by EPD |
|
2.4 |
Management Organizations |
|
|
2.5 |
Construction Works Schedule and Location Plans |
|
|
2.7 |
Marine Park Proposal |
|
|
2.8 |
Marine Ecology Conservation Plan |
|
|
2.9 |
Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for Construction and Associated Vessels |
|
|
2.10 |
Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for High Speed Ferries of SkyPier |
|
|
2.11 |
Marine Mammal Watching Plan |
|
|
2.12 |
Coral Translocation Plan |
|
|
2.13 |
Fisheries Management Plan |
|
|
2.14 |
Egretry Survey Plan |
|
|
2.15 |
Silt Curtain Deployment Plan |
|
|
2.17 |
Detailed Plan on Deep Cement Mixing |
|
|
2.16 |
Spill Response Plan |
|
|
2.19 |
Waste Management Plan |
|
|
3.1 |
Updated EM&A Manual |
|
|
3.4 |
Baseline Monitoring Reports |
7.7
Compliance with
Other Statutory Environmental Requirements
During the reporting period, environmental related licenses and permits required for the construction activities were checked. No non-compliance with environmental statutory requirements was recorded. The environmental licenses and permits which are valid in the reporting month are presented in Appendix E.
7.8
Analysis and
Interpretation of Complaints, Notification of Summons and Status of
Prosecutions
7.8.1
Complaints
An environment-related complaint was received on 24 April 2017 regarding dolphin watching arrangement for implementation of Dolphin Exclusion Zone (DEZ) in area of Contract 3204 for the period since early March 2017. Investigation was conducted by the ET in accordance with the Updated EM&A Manual and the Complaint Management Plan (CMP) of the Project. The ET’s review of checking records indicated that the DEZ monitoring arrangements of Contract 3204 for March and April 2017 were reviewed by the ET and IEC, based on the requirements of the DEZ Plan and prior to the Contractor’s implementations and noted the arrangements had followed the DEZ Plan. Furthermore, the implementation of DEZ was checked by the ET on-site during the regular and ad-hoc site inspections for Contract 3204 and noted the site practices had followed the proposed DEZ monitoring arrangements and in line with the DEZ Plan. Based on the investigation results, it is concluded that the 3204 Contractor deployed sufficient dolphin watching arrangements for implementation of DEZ during March and April 2017 and had followed the DEZ Plan. The complaint case was considered unfounded. Regular monitoring and mitigation measures will be continued.
Another environment-related complaint was received on 9 May 2017 regarding the intermittent release of exhaust air emissions from marine construction vessels of the Project. Investigation was conducted by the ET in accordance with the Manual and the CMP of the Project. The anonymous complainant did not provide any specific information (e.g. date/time) on the case or any details of the mentioned vessel types. There were no observations of dark smoke during ET’s site inspection in May 2017. ET will continue the regular auditing involves weekly and ad-hoc site inspections to, among other matters, check for any dark smoke emission from construction vessels, and to inspect vessel’s maintenance records. In case where dark smoke emission from a construction vessel is observed, the ET will require the concerned contractor to take immediate action to rectify the situation.
During the reporting period, another complaint was received on 22 May 2017 regarding discharges from construction vessel. The case is currently under investigation by the ET in accordance with the Manual and the CMP.
7.8.2
Notifications of Summons or Status of Prosecution
During the reporting period, neither notifications of summons nor prosecution were received.
7.8.3
Cumulative Statistics
Cumulative statistics on complaints, notifications of summons and status of prosecutions are summarized in Appendix F.
8 Future Key Issues and Other EIA & EM&A Issues
8.1
Construction Programme for the Coming Reporting Period
Key activities anticipated in the next reporting period for the Project will include the following:
Advanced Works:
Contract P560 (R) Aviation Fuel Pipeline Diversion Works
● HDD works; and
● Stockpiling of excavated materials from HDD operation.
DCM Works:
Contract 3201 to 3205 DCM Works
● Laying of geotextile and sand blanket; and
● DCM trials and works.
Reclamation Works:
Contract 3206 Main Reclamation Works
● Site office establishment; and
● Laying of sand blanket.
8.2
Key
Environmental Issues for the Coming Reporting Period
The key environmental issues for the Project in the coming reporting period expected to be associated with the construction activities include:
● Generation of dust from construction works and stockpiles;
● Noise from operating equipment and machinery on-site;
● Generation of site surface runoffs and wastewater from activities on-site;
● Water quality from laying of sand blankets and DCM works ;
● DEZ monitoring for DCM works and implementation of MMWP for silt curtain deployment by the contractors’ dolphin observers;
● Sorting, recycling, storage and disposal of general refuse and construction waste;
● Management of chemicals and avoidance of oil spillage on-site; and
● Acoustic decoupling measures for equipment on marine vessels.
The implementation of required mitigation measures by the contractors will be monitored by the ET.
8.3
Monitoring
Schedule for the Coming Reporting Period
A tentative schedule of the planned environmental monitoring work in the next reporting period is provided in Appendix B.
9
Conclusion and Recommendation
The key activities of the Project carried out in the reporting period included five DCM contracts, two advanced works contracts, and a reclamation contract. The DCM contracts involved DCM works and trials, site office establishment, laying of geotextile and sand blanket; the advanced works contracts involved articulated pipes installation, post laid burial work and concrete protection slabs installation, and HDD works; and the reclamation contract involved site office establishment and laying of sand blanket.
All the monitoring works for construction dust, construction noise, water quality, construction waste and CWD were conducted during the reporting period in accordance with the Updated EM&A Manual.
No exceedance of the Action or Limit Levels in relation to construction noise, construction waste and CWD monitoring was recorded in the reporting month.
Three exceedances cases involving Limit Level of 1-hour TSP were recorded during the reporting period. The investigation results indicated that the exceedances were possibly due to the adverse ambient air quality, but not related to the Project.
The water quality monitoring results for DO, turbidity, total alkalinity, SS, and chromium obtained during the reporting period were in compliance with their corresponding Action and Limit Levels stipulated in the EM&A programme for triggering the relevant investigation and follow-up procedures under the programmer if being exceeded. For nickel, some of the testing results exceeded the relevant Action or Limit Levels, and the corresponding investigations were conducted accordingly. The investigation findings concluded that the exceedances were not due to the Project.
Weekly site inspections of the construction works were carried out by the ET to audit the implementation of proper environmental pollution control and mitigation measures for the Project. Bi-weekly site inspections were also conducted by the IEC. Observations have been recorded in the site inspection checklists, including the observations on the conditions of silt curtains, which have been provided to the contractors together with the appropriate follow-up actions where necessary.
On the implementation of Marine Mammal Watching Plan, silt curtains were in place by the contractors for laying of sand blanket and dolphin observers were deployed in accordance with the plan. On the implementation of DEZ Plan, dolphin observers at 10 to 12 dolphin observation stations were deployed for continuous monitoring of the DEZ by all contractors for DCM and water jetting works for submarine cable diversion in accordance with the DEZ Plan. Trainings for the proposed dolphin observers were provided by the ET prior to the aforementioned works, with the training records kept by the ET. From the contractors’ MMWP observation records and DEZ monitoring records, no dolphin or other marine mammals were observed within or around the silt curtains, and no dolphins were sighted within the DEZ. These contractors’ records were checked by the ET during site inspection. Audits of acoustic decoupling for construction vessels were also carried out by the ET.
On the implementation of the Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for High Speed Ferries of SkyPier (the SkyPier Plan), the daily movements of all SkyPier high speed ferries (HSFs) in May 2017 were in the range of 91 to 97 daily movements, which are within the maximum daily cap of 125 daily movements. A total of 864 HSF movements under the SkyPier Plan were recorded in the reporting period. All HSFs had travelled through the Speed Control Zone (SCZ) with average speeds under 15 knots (7.8 to 14.0 knots), which were in compliance with the SkyPier Plan. Four ferry movements with minor deviation from the diverted route are under investigation by ET. The investigation result will be presented in the next monthly EM&A report. In summary, the ET and IEC have audited the HSF movements against the SkyPier Plan and conducted follow up investigation or actions accordingly.
On the implementation of the Marine Travel Routes and Management Plan for Construction and Associated Vessel (MTRMP-CAV), the upgraded Marine Surveillance System (MSS) was launched in March 2017. The MSS automatically recorded the deviation case such as speeding, entering no entry zone, not traveling through the designated gate. ET conducted checking to ensure the MSS records all deviation cases accurately. Training has been provided for the concerned skippers to facilitate them in familiarising with the requirements of the MTRMP-CAV. ET reminded contractors that all vessels shall avoid entering the Brothers Marine Park, which has been designated since 30 December 2016. 3-month rolling programmes for construction vessel activities were also received from contractors.


